When it comes time to manufacture a part, choosing between 3D printing and CNC machining can make a difference in cost, time, and results. Both technologies offer advantages, but understanding which one best suits your project will undoubtedly make a difference in the outcome.
At Atienza & Climent, as specialists in industrial solutions, we explain how to choose the right method. If you still have questions, consult with our mold manufacturing experts; they will advise you on every step of the process.
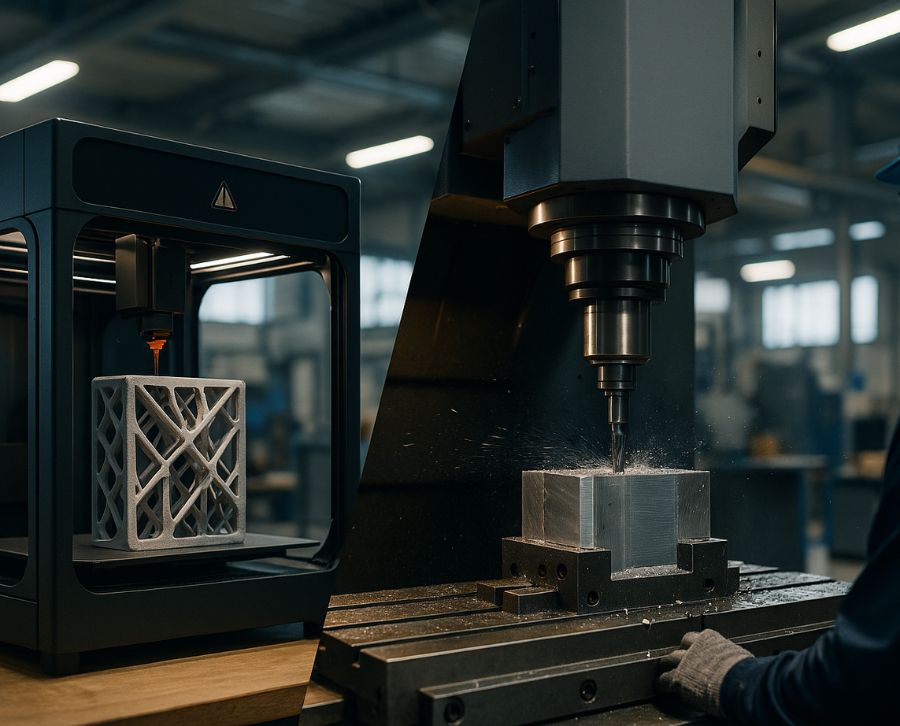

The key decision: additive (3D) vs. subtractive (CNC) manufacturing
When faced with the challenge of developing a new product, one of the most important aspects is deciding how to manufacture it. This is an important choice, as it directly affects cost, timescale, and final quality.
There are two main options: additive or subtractive manufacturing. Each has its advantages, limitations, and specific applications. Choosing the right technology will speed up the process, make better use of resources, and ensure the product meets your expectations from the start.
What is additive manufacturing and how does it work?
In this manufacturing process, the material is built layer by layer. Unlike traditional methods, this method doesn’t start with a block of material that is carved, but rather generates only what’s needed in a controlled, step-by-step manner.
One of the main advantages of this process is its speed, as it reduces intermediate times such as tooling production, resulting in parts produced up to 90% faster than traditional methods.
Furthermore, by using only the necessary materials, there is no waste, which is why the cost is lower, and the production is also environmentally friendly.
3D rapid prototyping is very common in this method, a technique that allows designs to be validated, shapes to be adjusted, and the functionality of a part to be verified before going into production.
What is subtractive manufacturing and what is its principle?
Unlike the former, subtractive manufacturing follows a more traditional but no less efficient approach. Here, the starting point is a solid block of material that is gradually removed and carved until the exact desired shape is achieved.
It’s one of the most widely used methods, especially when working with materials such as metal or wood. It can be done manually or using CNC machining, the latter being the most effective and efficient option.
Over time, this method of production has been updated, allowing for previously unimaginable levels of precision. All of this results in perfectly finished parts that are also highly resistant and durable.
Analysis of industrial 3D printing (Additive Manufacturing)
Additive manufacturing, or industrial 3D printing, offers certain advantages over traditional methods. But it’s not all in its favor; there are also disadvantages and limitations that you need to be aware of if you’re considering this production method:
Advantages: speed, geometric freedom and cost in low series
Without a doubt, its strength is speed. Thanks to 3D rapid prototyping, a product can be created piece by piece without intermediate processes; it can go from a digitalized design to a physical part in just a few hours.
It also allows for the creation of geometric shapes that would be unthinkable in traditional production, from rounded surfaces to complex finishes, all in a single design.
Furthermore, the ability to manufacture parts using this digital process allows for a reduction in production costs, especially in terms of storage and logistics. This allows for virtual stock availability and the required part can be manufactured immediately, without having to store it in a physical location.
Limitations: mechanical properties and surface finishes
But it’s not all advantages. Some 3D-printed parts aren’t as durable as those made using traditional methods. Furthermore, reliability cannot be guaranteed when repeating the process. This means that the parts may not always be of the same quality, especially in terms of hardness and flexibility. Therefore, it’s a method that requires constant supervision.
Added to this is the fact that the current cost of industrial-scale 3D machinery is high. Manufacturing using this method requires a large initial investment. However, like all innovative products, its price is expected to decrease as the technology becomes more widely used.
Ideal Applications for 3D Prototyping
3D additive manufacturing is primarily used in the production of custom parts, as it allows complete freedom in the design of shapes and surfaces. It is also ideal for small-scale production, which is especially useful for niche products.
It’s especially useful when you need to validate a project without a significant investment. It’s useful for presenting an idea, studying its ergonomics, or determining whether it fits as expected.
Analysis of CNC Machining (Subtractive Manufacturing)
The traditional subtractive production method, also known as CNC turning, is the most widely used due to its long-standing popularity. However, like the previous method, its application has both advantages and limitations that must be taken into account:
Advantages: high precision, strength and final materials
Parts manufactured using a CNC machining center are strong and highly durable. Unlike most 3D processes that rely on heat, this manufacturing process allows parts to be built at room temperature, allowing for product designs with millimeter precision in every component.
Limitations: Design restrictions and material waste
However, subtractive manufacturing isn’t suitable for every design. Very complex shapes or those with internal voids often require a significant amount of adjustment to achieve the desired result.
Furthermore, when working by cutting and removing material, there is a certain amount of waste that is inevitable. This makes this method not the most economically efficient.
Ideal applications for CNC prototyping
CNC lathe machining is perfect for validating parts that perform like the final version. It’s suitable for harder materials such as wood or steel.
Furthermore, it is very useful when the prototype needs to be tested under conditions exactly the same as real ones.
Direct Comparison: Which technology wins in each scenario?
Now that you know the differences between additive 3D printing and subtractive manufacturing, you can understand which technology is best suited for your production scenario:
Speed: Rapid prototyping vs. robust parts
If what you need is rapid production, then the most suitable method is 3D printing, as it is much faster compared to traditional methods.
However, if you’re looking for a finish with great durability and strength, you’ll need to opt for lathe machining, which ensures that each project is especially robust in every component.
Cost: Complex geometries vs. Simplicity of the part
The cost depends primarily on the shape and quantity. For unique or highly elaborate parts, additive manufacturing may be more cost-effective. However, if the design is simple and will be repeated many times, CNC machining will be less expensive.
Precision and Tolerances: What level of accuracy do you need?
The CNC machining center is, without a doubt, the most accurate and precise method. Therefore, if you’re looking for millimeter accuracy, this production method will be the most convenient. If, on the other hand, a purely visual or validation project is required, 3D manufacturing may be a more than acceptable option.
Strength and Materials: Visual vs. Functional Prototypes
If you’re looking to test the behavior of a part subjected to specific forces or temperatures, a 5-axis machining center is the most comprehensive option. It allows you to work with technical materials that exactly reproduce the behavior of the final product.
Design Freedom: Organic Shapes vs. Prismatic Geometries
Freedom in project design is a very important factor to consider. If your part is complex or includes complicated geometric shapes, 3D manufacturing gives you that freedom. If, on the other hand, you work with conventional shapes, machining can solve them easily and more quickly.
Need help choosing? Your project is in expert hands.
If you’re still unsure which process to choose, don’t worry; it may seem complicated at first. At Atienza & Climent, we’ll help you choose the process that best suits your needs. You’ll always have support and advice throughout every step of the process.
Our technical team works with trusted suppliers like Tecnoval Mecanizados, allowing us to handle projects with full guarantees. We have the tools to handle everything from single-series CNC components to full production batches with complete dimensional control.
We analyze the viability of your piece and recommend the best technology.
The important thing isn’t which machine to use, but which solution is best suited for your specific product. At Atienza & Climent, we analyze each design and adapt it to the process that best suits you. Sometimes you can combine both methods: prototyping with 3D printing and then validating with 5-axis milling. Or you can start with a functional model and move it to production on a machining center.
Sometimes, it’s not about choosing between one or the other. It’s about knowing when to use each technology to take advantage of the best of both.
Preguntas frecuentes sobre la impresión 3d vs la mecanización CNC
La 3D construye capas de material; el CNC parte de un bloque y elimina material hasta la forma final.
Cuando priman rapidez, libertad geométrica y series cortas o personalizadas. Ideal para validar diseño y ergonomía.
Para piezas funcionales con alta precisión, tolerancias estrictas y materiales técnicos que deben comportarse como la pieza final.
Impresión 3D: pasa del diseño digital a pieza física en horas, sin utillajes.
Depende de forma y cantidad: 3D rinde en piezas únicas/geométricas complejas; CNC compensa en diseños simples y repetitivos.
El CNC es la referencia en exactitud dimensional y consistencia entre piezas.
CNC: piezas más robustas y con mejor acabado superficial; 3D puede requerir posprocesos y no siempre iguala propiedades finales.