If you have ever wondered how those complex-shaped plastic parts are made and how they are so strong, you have probably appreciated the result of the rotomoulding process. This manufacturing technique, also known as rotational moulding, has gained popularity in various industries thanks to its unique advantages and versatility in creating plastic products.
At Atienza & Climent, as one of the companies that carry out this technique, we will explain in detail in this article the rotational moulding process, its advantages and uses in different sectors, as well as the materials used, key techniques and innovations that are shaping the future of this technique.
What is rotomoulding? Definition and basic concept
In essence, rotomoulding is a process that involves rotating a mould loaded with plastic material in three dimensions in an oven. As the mould rotates, the plastic adheres to the inner walls of the mould due to centrifugal force, creating a uniform layer. The mould is then cooled and the finished part is removed.
This technique is particularly useful for producing large, complex objects that would be difficult to manufacture using other methods.
Advantages and characteristics of rotomoulding
This technique offers a number of significant advantages that make it attractive for the manufacture of a wide range of products.
One of its main advantages is the ability to create large parts and complex shapes without the need for expensive, high-precision moulds. In addition, this process allows for efficient and cost-effective production, reducing material waste.
The versatility of rotomoulding allows the design of bespoke products that meet the highest standards of durability and strength. Our experience in the industry has shown that this technique is key to producing high quality plastic parts that exceed our customers’ expectations.
Rotomoulding process
The rotomoulding process consists of several key steps that ensure quality and precision in production.
Preparation of moulds and materials in rotational moulding
Before starting the rotomoulding process, it is essential to prepare suitable moulds. These moulds can be made of aluminium, stainless steel or even high-strength synthetic materials. Once the mould is selected, a specific amount of plastic material is added, usually in the form of powder or granules, and its uniform distribution inside the mould is ensured.
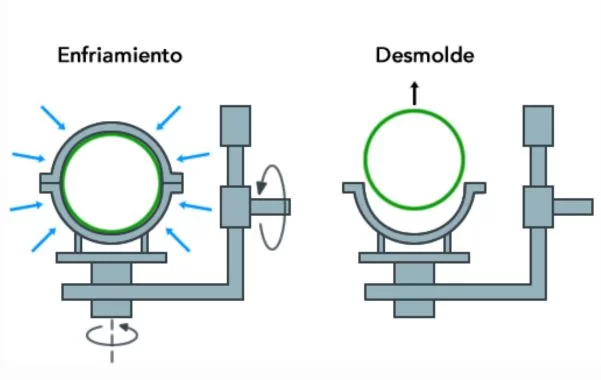
Rotomoulding process stages: loading, heating, cooling, demoulding and demoulding
With the moulds loaded, the process begins. The mould is placed in a rotomoulding machine, where it begins to rotate on multiple axes. During rotation, the mould is heated in an oven, which causes the plastic to melt and then adhere to the inner walls of the mould.
Once the heating process is complete, the mould is gradually cooled to solidify the plastic. Finally, the mould is removed and the finished part is removed.
Rotomoulding uses
This method has multiple industrial uses, thanks to its versatility and ability to create products with unique and functional shapes.
Rotomoulding in the plastics industry: containers, tanks and industrial products
In the plastics industry, it is used to manufacture containers, tanks and industrial products. Its ability to produce large hollow parts with uniform thickness and corrosion resistance makes it an ideal choice for storing chemicals and liquids.
Rotomoulding in the automotive industry: durable parts and components
In the automotive industry, it is used to create durable parts and components such as bumpers, fuel tanks and interior components. The resistance of plastic produced by rotational moulding to impact and exposure to the elements makes it highly suitable for these applications.
Rotomoulding in the leisure and sports sector: toys, furniture and equipment
In the leisure and sports sector, it brings toys, furniture and equipment to life. From slides and play structures to garden furniture, rotomoulding offers safe and durable products that can withstand constant wear and tear.
Rotomoulding in the construction industry: architectural and infrastructure elements
It also has a place in the construction industry, where it is used to create architectural elements, waste containers and infrastructure components.
The durability and weather resistance of rotomoulded parts make them suitable for using in challenging environments.
Materials used in rotomoulding
Various plastic materials are used which can be used to suit different requirements and technical characteristics of the final product.
Polyethylene and its variants in rotomoulding
Polyethylene is one of the most widely used materials in rotational moulding due to its versatility and strength. Common types of polyethylene include LDPE (low density polyethylene) and HDPE (high density polyethylene). Each variant offers specific properties to suit the needs of the use.
Other common materials in the rotomoulding process
In addition to polyethylene, other materials such as PVC, polypropylene and nylon can be used in the rotomoulding process to achieve particular properties, such as chemical resistance or flame retardant characteristics.
Techniques and considerations in rotomoulding
The art of rotomoulding goes beyond simple rotation. Designing efficient moulds and optimising the process are crucial to ensure high quality and efficient results.
Mould design for rotomoulding
The basis of a successful rotomoulded product lies in the right mould design.
The shape, geometry and texture of the moulds play a crucial role in the quality and functionality of the final part. A well thought-out design not only ensures a smooth demoulding, but also affects the thickness distribution of the plastic during the process.
The demoulding angle is a vital consideration. An optimum angle facilitates the removal of the moulded part, preventing deformation or damage. In addition, consideration must be given to the uniformity of the plastic thickness to ensure that the final product is consistent and strong throughout.
Optimising times and temperatures in the rotomoulding process
Precision in the management of thermal factors is key when carrying out this technique. The process involves three key stages: loading, heating and cooling.
Initial loading of the plastic powder must be uniform to achieve homogeneous distribution. Heating, often controlled by zones in the oven, must be gradual and precise. The right temperature allows the plastic to melt smoothly and adhere to the mould.
Cooling is also essential. Controlled and gradual cooling prevents internal stresses and deformations in the moulded part. Here, the right combination of time and temperature is crucial to achieve a defect-free final part. Optimising these factors not only improves product quality, but also increases process efficiency, allowing for shorter production cycles.
Innovations and trends in rotomoulding
The world of rotomoulding is constantly evolving, with new technologies and approaches broadening its horizons. Join me as we explore some of the latest trends and exciting developments in the field.
Advances in materials and technologies in rotomoulding
The search for more sustainable materials and advanced production techniques is driving innovation in rotational moulding. From fibre-reinforced composites to biodegradable materials, the industry is taking a more eco-friendly approach.
Sustainability and energy efficiency in rotomoulding
The use of sustainable techniques in any manufacturing process has become a mainstay in all industries, and rotational moulding is no stranger to this trend. Manufacturers are adopting more sustainable practices throughout the process, from the choice of materials to waste management.
In terms of materials, the search for biodegradable and recyclable alternatives is in full swing. Bioplastics and recycled resins are being successfully incorporated into the rotational moulding process, reducing reliance on virgin materials and reducing environmental impact.
Future of rotomoulding
If we talk about the future of this field, we can see how it is facing new possibilities and innovations. As we move into the age of modern manufacturing, this process continues to evolve and adapt to meet the changing demands of various industries.
Growth potential and new applications for rotomoulding
As technology continues to advance, rotomoulding is expanding its reach into new applications and sectors. From the medical industry to fashion and design, the growth potential for rotomoulding is endless.
Imagine the possibility of creating customised medical implants through rotomoulding, or the creation of unique and sustainable fashion pieces. The flexibility of the process allows you to explore uncharted territory and respond to changing market demands.
Research and development in the field of rotomoulding
Research and development continues to drive remarkable advances in the field of rotomoulding. Exploration of new materials, process optimisation and implementation of cutting-edge technologies are taking the process to higher levels.
Current research is focused on improving the energy efficiency of the process, reducing waste and creating biodegradable materials that align with the demands of a more environmentally conscious world.
The future of this process is promising and inspires us to continue to explore, innovate and create solutions that will ensure a brighter and more sustainable tomorrow.
Interested in discovering how rotomoulding can transform your ideas into reality? Contact us and together we will explore the endless possibilities that this exciting process offers!




 by
by