Do you know how the plastic products in your home are made? The answer lies in rotomolding, injection molding, and die-cutting. Here at Atienza & Climent, we have more than three decades of experience in production, and that’s why we want to help you choose the best one for your business.

Introduction to manufacturing processes
Are you familiar with terms like rotational molding and die-cutting? These define a large part of manufacturing worldwide. Of course, it can be difficult to choose the best option.
In this guide, you’ll learn the in-depth characteristics of each process. This way, you’ll have a clear idea of which one to choose based on your context.
Importance of choosing the right process and its impact on the final product
Why is it so important to make the right decision? This will affect efficiency and resource expenditure. There are cases in which rotomolding and thermoforming should be used. Using the wrong method can lead to additional expenses.
Rotomolding: definition, operation and uses
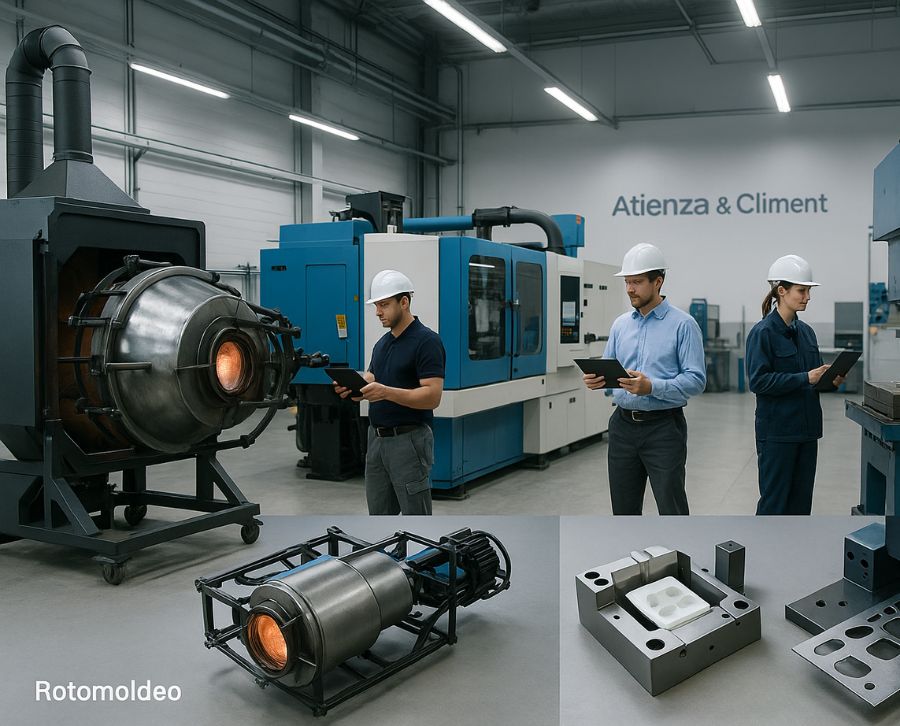
Let’s start with rotational molding. A process that could be summed up as highly sustainable and with a wide variety of uses.
What is the rotational molding process?
This process begins by introducing powdered plastic into a metal mold and heating it to 300°C. At the same time, the mold is rotated on its vertical and horizontal axes to distribute the plastic.
The next step in plastic rotational molding is cooling, which occurs while the mold continues to rotate. Finally, the finished part is removed.
Materials and tools for rotational molding
Plastic is the star of this process. Rotomolding materials are typically plastisol, polypropylene, and polyethylene. They are characterized by their resistance to impacts and temperatures up to 140°C.
The molds used for rotomolding in Spain are typically made of steel and aluminum. In addition, rotational machines are used to spin the molds and ovens capable of heating up to 450°C.
What does a rotational molding operator do?
Now that you know what rotational molding is, it’s time to learn about the operators’ jobs. They are responsible for cleaning rotational molds, loading plastic material into them, and adjusting temperature and rotation speed parameters.
They must also remove products from the process. They detect errors and ensure everything is in order.
Advantages and disadvantages of rotational molding
Are there all the advantages of rotational molding? Certainly, the molds are more economical, and there is a wider range of manufacturing sizes. It also stands out because it doesn’t waste much plastic.
However, this process also has its drawbacks. The cycles are slower and don’t usually accept a wide variety of raw materials. Furthermore, mold wear is one of its main weaknesses.
What can be manufactured with rotational molding?
The versatility of plastic rotational molding cannot be denied. It can be used to manufacture tanks, chairs, benches, wastebaskets, and flower pots.
Playground equipment such as slides and swings can also be manufactured. In the automotive and general machinery industries, all types of parts can be manufactured with rotational molding polyethylene.
Injection molding: optimization and comparison
Now we move on to a second manufacturing process. Perhaps the main difference from the first is its ability to increase the serial number.
Basic steps of injection molding
Injection begins by holding the two halves of the mold together to seal them tightly. The injection machine is then used, which has a screw that pushes the molten plastic into the mold.
The screw then reduces its speed but maintains high pressure to compensate for the shrinkage of the plastic as it cools. Cooling is done with water or oil, and finally, the mold is opened to remove the part.
Techniques to optimize temperature, pressure and times
Product quality and production time depend on improving several variables. This includes setting different temperature levels to reduce degradation and adjusting high pressure at the beginning of injection.
Automation is also key to eliminating downtime. New strategies to optimize the production of plastic products are expected in the future.
Rotomolding vs. Injection: When to Choose Each
Now, rotational molding vs. injection molding: when should you use one or the other? Here’s a brief comparison:
Variable | Rotomolding | Injection |
Output | Up to 3,000 units per year | More than 10,000 units per year |
Production cost | High or low depending on whether the volume is low or medium | Very low if the volume is high |
Piece size | Up to 300 gallons (Tank) | About 5 gallons |
Initial cost | Fairly economical mold design | Expensive molds to design |
Now that we’re familiar with injection molding, rotational molding, and thermoforming, it’s time to talk about the die-cutting method.
Concept and types of die-cutting
Die-cutting uses a tool called a die. This tool cuts, perforates, or deforms the plastic to make a new part. Cuts or perforations are typically made using punches.
There is also stamping die-cutting, which uses compressive force to deform the plastic. Finally, precision die-cutting allows for smooth edges.
Advantages and disadvantages of die-cutting
Die-cutting is a rather interesting manufacturing process. After all, it’s automated, allowing thousands of parts to be created in a short time with great precision. It also saves up to 20% on material.
And while there are some good things, there are also things that could be improved. Dies are very expensive, and designers must work harder to create designs that fit the die.
Applications and products obtained by die-cutting
What can die-cutting be used for? Unlike rotomolding, it has applications such as complex designs for toys, gears, and wheels.
It can also be used to make packaging and protective packaging. The precision of die-cutting is excellent for creating keychains, zippers, and 3D prints.
Mold texturing and surface finishes
While rotational molding with recycled plastic and other processes focus on creating shapes, texturizing focuses on finishing. It uses physical and chemical processes to transform the surface of plastic parts.
Texturizing methods
There are also several types of texturing to recreate cool designs on plastic. There’s chemical etching with nitric acid or ferric chloride, and laser texturing.
Sandblasting texturing is also a good option. It uses glass stones or aluminum oxide, producing an abrasive process that creates roughness.
Surface finishes: polishing, painting and coatings
Finally, finishing procedures are used for texturing. This can be achieved by polishing the surface with sandpaper and brushes, or by painting with liquid or powder coatings.
In some cases, metallic coatings are used. These are excellent for creating elegant finishing effects.
Conclusions and guide to choosing the right process
There is no single procedure that is better than another. Each has its pros and cons and depends solely on the product being manufactured.
Decision factors
Which one should I choose? Below is a chart to help you make the best decision.
Parameter | Rotomolding | Injection | Die cut |
Output | Low and medium | High | High |
Piece complexity | Large hollow pieces | Complex geometries | Parts with tight tolerances |
Cost | Low | Medium – High | very high |
Available materials | Limited to thermoplastic powders | Supports non-ferrous metals | Wide variety of thermoplastics |
Final recommendations and contact
And if you’re unsure whether to choose rotational molding or another process, you can get the best advice at Atienza & Climent. After all, a bad decision can cost you a lot of money. Choose the best option for your needs.
Frequently asked questions about manufacturing processes, rotational molding, injection molding, and die-cutting.
Rotomolding is a process in which powdered plastic is introduced into a metal mold that rotates on two axes while being heated. This allows for the production of strong, hollow parts, such as tanks, reservoirs, flowerpots, or street furniture, with minimal material waste.
The most common materials are polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and plastisol, due to their high impact resistance and resistance to temperatures of up to 140°C. Molds are usually made of steel or aluminum, which can withstand the heat of industrial ovens.
Rotomolding stands out for its low mold costs, high durability, large-part production, and sustainability, as it generates little plastic waste. However, it is slower than injection molding and offers less variety in materials.
Injection molding involves melting plastic and forcing it into a closed mold using a screw. Once the material cools, the mold is opened and the final part is removed. It is the ideal method for manufacturing high-volume, complex, and highly precise parts.
Rotomolding is best for large, hollow parts with low to medium production runs, while injection molding is ideal for high-volume runs of small parts or parts with complex geometries.
In short: Rotomolding = versatility; injection molding = mass efficiency.
Die-cutting uses a tool called a die, which cuts, perforates, or deforms the plastic using pressure. It is used in high-production automated processes to produce parts with precise edges or embossed details, such as packaging, toys, or industrial components.