Plastics are present in our daily lives. We use them as food packaging; the casing of our smartphone and some important parts of our car are also made of some kind of plastic. But how are the parts we see and use every day made?
There are different processes for making plastic parts. Depending on the type of object and the material used, each has its own advantages and disadvantages. In this guide we talk about the eight most commonly used processes at an industrial level.

Types of plastic parts
To begin with, we will differentiate plastic parts into two main groups according to their thermal behaviour: thermoplastics and thermosets.
Thermoplastics soften when heated and harden when cooled. They can be easily recycled. Examples include PVC, polyethylene, nylon, acetates, methacrylates, etc.
Thermosets, on the other hand, can only be moulded once, if re-melting is attempted, they will burn. Therefore, they are not recyclable. Some examples of thermosets: epoxy resins, Bakelite, polyester.
Thermoplastics are definitely the most widely used, accounting for more than 80% of the total volume. They are suitable for most processes.
On the other hand, plastic parts can also be classified according to their shape or size:
- Hollow: bottles, tanks, pipes.
Solid: handles, holders, protectors.
- Thin: sheets, films, bags.
Small: gears, connectors.
- Large: tanks, reservoirs, etc.
It is important to be aware of these differences, as not all processes can use thermosets or be used to make any shape.
Plastic parts manufacturing processes
Therefore, each plastic parts manufacturing process has its strengths compared to others in terms of its capacity to produce certain geometries, tolerances, finishes, production volumes, etc.
Knowing the advantages and limitations of each technique is of great help when choosing the most suitable manufacturing process for each type of part to be produced.
Injection moulding
Plastic injection moulding is one of the most versatile and precise processes. The molten thermoplastic is injected under pressure into a closed mould where it solidifies into the desired shape.
Injection moulding can be used to produce many types of parts with complex shapes: housings, mechanical parts, toys, etc.
It is ideal for producing large series quickly and efficiently.
Extrusion
Plastic extrusion consists of passing the molten polymer through a die to give it the desired shape.
It is ideal for producing profiles, tubes, sheets, coatings and plastic films. It allows for the continuous production of hollow and thin parts.
Blow moulding
In blow moulding of plastics, a preform in the form of a tube is normally heated until it softens. Pressurised air is then introduced to expand the tube against the walls of a mould into a hollow shape.
This process is used to make a variety of products such as bottles, hollow toys, tanks, etc. It is very versatile for producing hollow thermoplastic parts.
Thermoforming
In thermoforming, sheets of thermoplastic are heated and then shaped by vacuum, mechanical or manual pressure.
It is used to produce trays, cases, containers, housings, etc. It is ideal for producing shallow-shaped parts quickly and economically.
Rotomoulding
Rotomoulding involves placing plastic powder into a hollow mould that rotates on two axes while it is heated. The polymer adheres to the walls of the mould and takes its shape.
This method makes it possible to obtain small, medium or large hollow parts, such as water tanks, motor casings, toys, etc. It is versatile and economical for small-scale production.
Injection blow moulding
Injection blow moulding combines both processes. Plastic is first injected into a mould to create a preform, then heated and expanded by blowing.
It is used to produce thin-walled containers such as jars or bottles. It allows the production of highly accurate and complex hollow parts with excellent finish.
CNC machining
CNC machining uses computer-controlled machines to cut, drill or sculpt blocks of plastic into the desired shape and finish.
It is ideal for producing prototypes, or short runs with high precision, complexity and detail that other processes cannot achieve.
It is also ideal for creating moulds or decorative parts with endless possibilities.
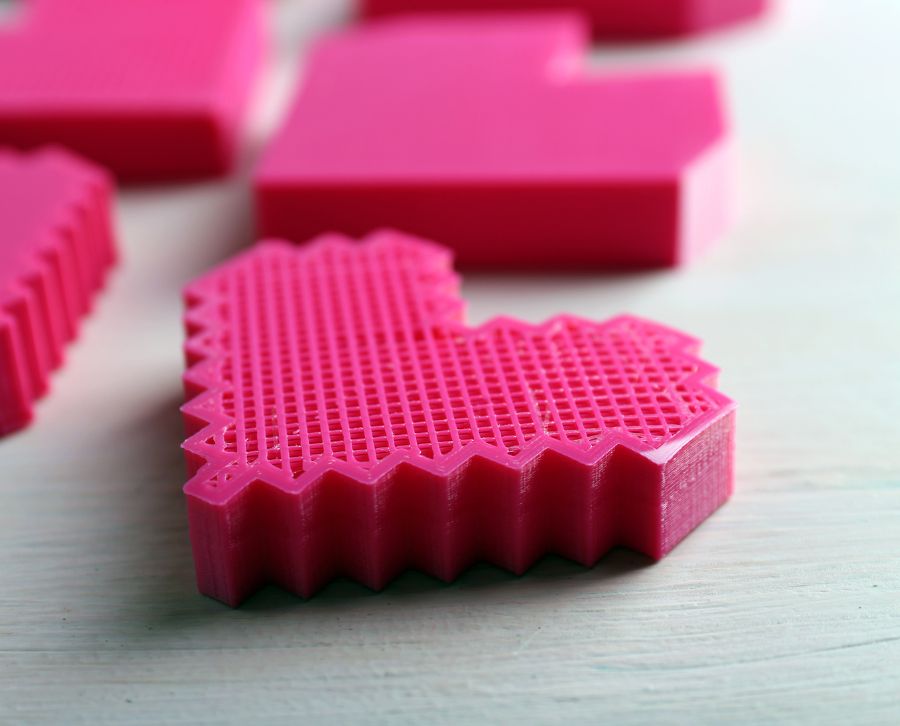
3D Printing
3D printing is one of the most up-to-date processes. It builds the part layer by layer by depositing the molten material following a digital model.
It makes it possible to manufacture single parts, short series, prototypes and models without using moulds, although at a slower speed than injection moulding. It offers total geometric freedom for complex designs.
What is the best process for creating plastic parts?
There is no single ideal process for making any type of plastic part. Each technique has its advantages and disadvantages. Some are faster, some are more precise and some are somewhere in between.
The choice will ultimately depend on the type of plastic, the shape, the size, the size of the series and the precision required for each part.
In short, there is a wide variety of plastic processes that offer great versatility to create almost any object.





 by
by