Rapid prototyping is a very useful process that allows you to speed up the process of testing, designing and validating new product ideas before you launch them on the market. Thanks to this, you can quickly create your tests, using different types of materials, although plastics such as ABS, polycarbonate or polypropylene are the most commonly used.
You can get many benefits from this trendy technology, including reduced costs and development time, as you can correct the design before final production. In addition, you can test the functionality of the product and validate whether it will be viable.
This is why it is a widely used solution in the electronics industry or as a process prior to the manufacture of machinery. This is because it considerably accelerates the entire process of conceptualisation, design and testing.
Now that you know what it consists of, it is time for you to get to know the six most commonly used techniques for rapid prototyping.
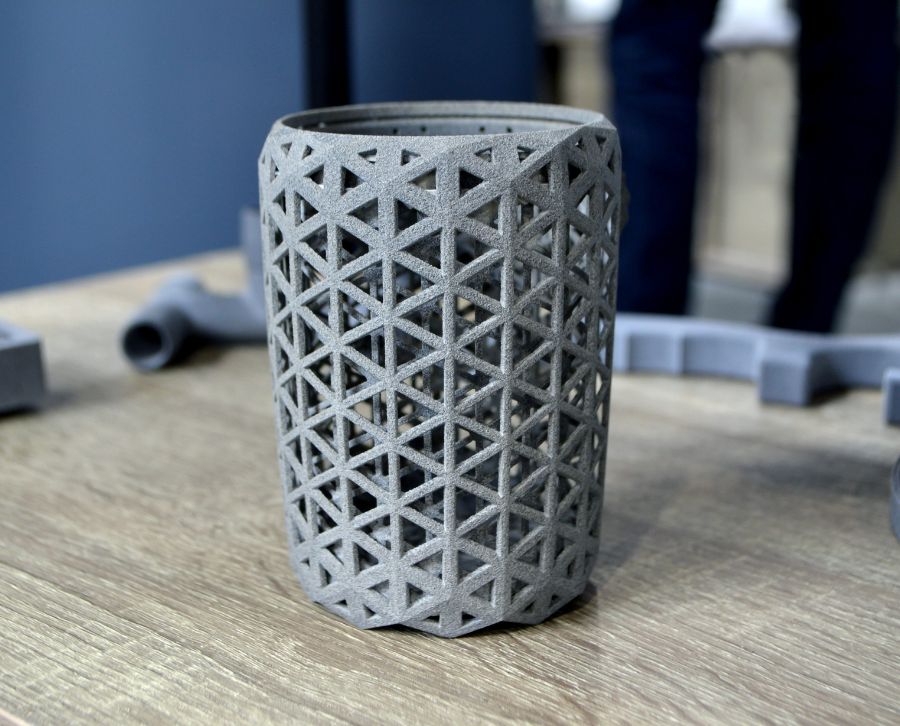

Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM)
FDM technology is one of the best known additive manufacturing methods. It is based on the deposition of molten material layer by layer to create the object. The most common materials are ABS and PLA, the latter being a more sustainable and biodegradable option. Other materials such as PET, PETG or nylon can also be used.
FDM printers allow you to create parts with good mechanical strength quickly and economically. They are ideal for creating conceptual prototypes and scale models. They allow you to test shapes, assemblies and functionalities in a very agile way.
Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography (SLA) is another additive manufacturing technique that may be of interest to you. SLA printing machines cure liquid resin layer by layer using ultraviolet light.
This technique produces parts with higher resolution and dimensional accuracy than FDM printing. It uses materials such as PLA, ABS, TPU, nylon and even ABS medical, certified by ISO 10993-1.
Stereolithography is ideal for creating prototypes that require fine details, a good finish and good mechanical strength. It is used in sectors such as jewellery and automotive.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is another versatile additive manufacturing technology. Instead of melting or curing material, the laser sinters powder layer by layer in a solid state.
The most common materials are nylon, PP and TPE, but there are others you can use depending on what you are looking for.
SLS allows you to create tough and functional prototypes with good detail and precision.
It is ideal for creating concepts and scale models that require mechanical strength and fine detail.
Computer Numerical Control (CNC)
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) refers to a set of machines that are operated by computer-controlled commands, such as laser cutting, CNC milling or CNC turning.
These technologies allow samples, mock-ups or pre-series to be created quickly and accurately, in a variety of materials such as wood, plastics, metals, ceramics and composites. It is used to create prototypes, but also high quality final parts.
Laser cutting and engraving is perfect for creating 2D shapes with great precision and detail, while CNC milling and turning allows more complex 3D geometries to be created.
Rapid injection moulding
This variant of injection moulding allows you to create plastic parts very quickly by creating temporary moulds using additive manufacturing.
Instead of using the usual permanent steel moulds, plastic or resin moulds are printed using technologies such as FDM or SLA. This speeds up the time and reduces the cost of the process.
It is ideal for producing small series of final parts or functional prototypes with the same properties as the final plastic. It allows testing of shapes, colours and final product properties.
Laser cutting and engraving
With this technique you can create 2D shapes with great precision and detail on materials such as wood, paper, plastic, fabric, leather or metal, among others.
By programming the laser path, you can create parts with unique shapes in a fast and repeatable way. It is ideal for creating concept models, mockups, templates and other prototypes.
3D scanner technologies
We leave for the end a technology that allows the creation of the computer model prior to prototyping. 3D scanners can digitise physical objects and obtain their virtual replica in 3D. There are different technologies: structured light, laser or photogrammetry.
With these you can scan existing products, unique parts or even people and generate 3D models that are modifiable and ready to print.
3D scanners are essential for product development, to replicate existing geometries or create custom replicas. They speed up design time and enable faster and more accurate prototyping.
Conclusion
As you have read here, there are multiple technologies for rapid prototyping. From FDM or SLA 3D printing, to CNC, to techniques such as laser cutting or 3D scanning.
The key here is to choose the technology that best suits the characteristics of the prototype you need, such as strength, precision, materials and finishes. Good rapid prototyping usually combines several technologies.



 by
by