Have you ever wondered how so many toys and other products are mass-produced with such precision? The answer to this question is simple: thanks to the use of moulds.
Moulds are essential tools for creating multiple identical copies of a design by injecting the desired material (plastic, metal and others) by different processes and types of moulding, such as blow moulding or vacuum moulding. This mass production technique has been around since the Second Industrial Revolution (19th century) and has been perfected for more than 150 years.
There is no doubt that the toy industry would be very different if moulding did not exist. Although there are more modern manufacturing processes, such as additive manufacturing by 3D printing, they do not yet allow for such cost-effective large-scale production in such a short time.
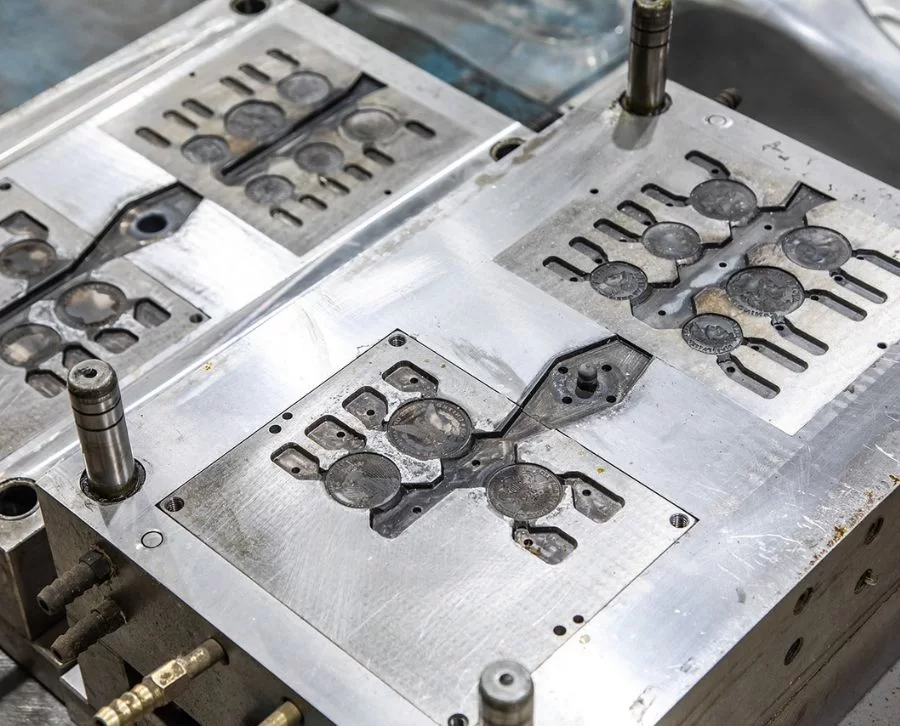

Injection moulds
Injection moulds (or injection dies) are the production system used to create many of the toys you see in shops, as well as other plastic or metal products. They are an efficient way to produce all kinds of parts and components for the final assembly of toys and utensils.
How conventional injection moulding works is simple: you need a mould and an injectable material that can be melted and re-solidified, such as plastic.
The mould consists of two plates, which together create the negative shape of the part. An injection moulding machine pumps the molten thermoplastic into the mould at high pressure through a feed channel, where it quickly takes the shape of the cavity as it cools in contact with the cold walls of the mould.
Once the part is solid, the mould is opened and extracted, to close it again and start a new automatic cycle of injection, cooling and ejection. In this way, plastic parts or toys can be manufactured in series and at high speed with precision and quality.
There is no single type of injection mould. Depending on the complexity of the part or the final finish, the following variations can be used.
Two-plate mould
The two-plate mould is the simplest mould. It consists of two half dies that are joined together to form the part. It is used for simple, symmetrical objects.
Three-plate mould
The three-plate mould incorporates a third movable plate that allows more complex objects to be created with internal areas that are inaccessible with only two parts.
Cold runner mould
The cold runner mould has separate cooling channels for faster and more homogeneous cooling. It has the advantage of allowing shorter injection cycles.
Hot runner mould
In this case, critical areas are selectively heated to prevent premature cooling of certain areas, improving filling.
Family mould
The family mould contains several moulds of the same part on the same base part. It optimises series production.
Over-injection mould
Injects a second layer of material over the base part. Used for parts with areas of different colour or material.
Insert mould
Inserts are manually placed inside the insert mould before each injection cycle. To include metal parts, for example.
Rotational mould
In this variant, the part rotates during injection moulding to create complex shapes and effects. It is used for toys and decorative parts.
Comparison of mould types
Below, we compare the different types of moulds used in the toy manufacturing industry.
- Injection moulds: In the injection moulding process, molten plastic material is injected into a mould to shape the final product. This type of mould is versatile, economical and commonly used for the mass production of standard toys such as dolls and action figures. It is relatively easy to maintain, making it one of the most widely used options in toy manufacturing.
- Casting moulds: These can be made of sand, ceramic or metal and are ideal for complex metal parts or fine details. They are mainly used for toys that require a high level of realism, such as scale models of cars or aeroplanes. Metal casting processes offer the ability to manufacture high quality, strong and durable parts with an excellent level of detail.
- Stamping moulds: These moulds work by applying pressure between a die and a punch, allowing mass production at low cost. Stamping parts are more commonly used in other industries, but can also be used for the creation of toy components, such as helmets and armour or classic tin toys.
Other types of moulds:
- Rubber moulds: used to create toys in flexible rubber or rubber, they work by pouring and curing the material.
- Vacuum mould: ideal for complex geometries in hard plastics, such as building blocks.
- Zinc mould: specifically for zamak alloy, which is used in toy cars, trains and other metal parts.




 by
by